Healthcord Webinar Series
Difference between cord blood and cord tissue stem cells
Duration
4:00 minutes
Category
Stem cell basics
Series
Cord blood banking
Objective
Educational
What you will learn
- An introduction to embryonic development
- What is the placenta and why is it important?
- Components of the umbilical cord
- What is cord blood?
- What is cord tissue?
- Why you should choose to preserve both cord blood and cord tissue?
This lesson will introduce you to the placenta and the umbilical cord, highlight the difference between cord blood and cord tissue and why expectant parents should consider preserving both cord blood and cord tissue.
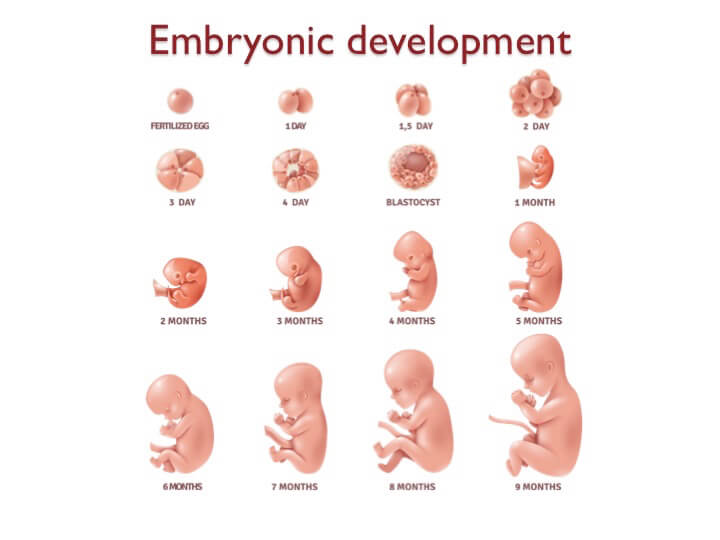 We will begin with a quick introduction to embryonic development. Once conceived, a baby goes through several different stages of development.
We will begin with a quick introduction to embryonic development. Once conceived, a baby goes through several different stages of development.
Every embryo begins as a single fertilized egg cell. Then within the span of a few weeks, this embryo establishes the basic body plan of an adult. Once the body plan is established, the embryo continues to grow and refine these basic features until fully developed.
All of these developmental events happen in utero or inside the womb of the mother and is only possible because of an amazing organ, the placenta.
The placenta is a temporary organ that grows during pregnancy. It is the only dispensable organ in the human body. The placenta attaches to the wall of the uterus and forms a connection between the mother and the developing baby.
 This connection is essential for providing the baby with the oxygen and the nutrients necessary for growth, and for removing the waste products from the baby’s blood. The blood vessels of the mother and the baby are found side-by-side in the placenta, keeping their blood supplies separate. The umbilical cord connects the growing baby to the mother.
This connection is essential for providing the baby with the oxygen and the nutrients necessary for growth, and for removing the waste products from the baby’s blood. The blood vessels of the mother and the baby are found side-by-side in the placenta, keeping their blood supplies separate. The umbilical cord connects the growing baby to the mother.
The umbilical cord itself has two components: cord blood and cord tissue.
Cord blood refers to the blood found within the umbilical cord and cord tissue actually refers to the umbilical cord itself. Given that the placenta is a temporary organ that develops during pregnancy, shortly after a baby is born, the body also expels the placenta.
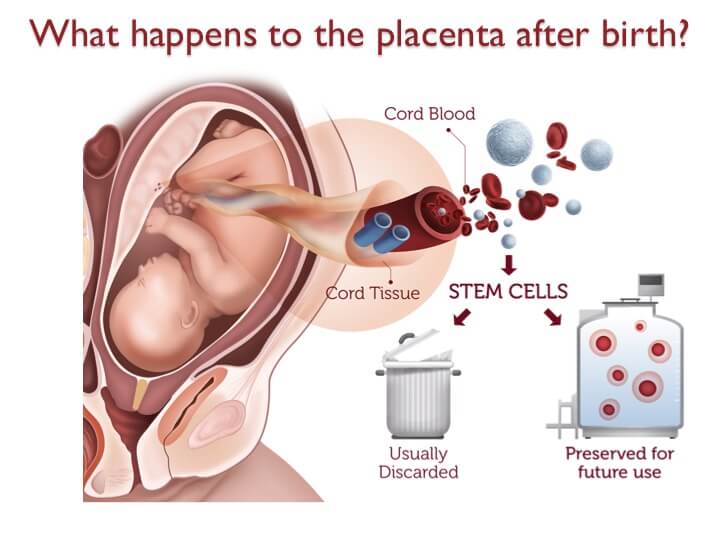 In the past, once the umbilical cord was cut, the cord and the placenta were discarded as medical waste. Today it is well established that cord blood, cord tissue and even the placental are sources of valuable stem cells, and when possible, should be preserved.
In the past, once the umbilical cord was cut, the cord and the placenta were discarded as medical waste. Today it is well established that cord blood, cord tissue and even the placental are sources of valuable stem cells, and when possible, should be preserved.
Cord blood and cord tissue are sources of at least two different types of stem cells, which is why many expectant parents choose to preserve both cord blood and cord tissue.
Cord blood is a source of hematopoietic stem cells. These cells produce different types of blood cells and immune cells in our bodies.
They are useful for treating blood-related diseases and for replenishing the immune system.
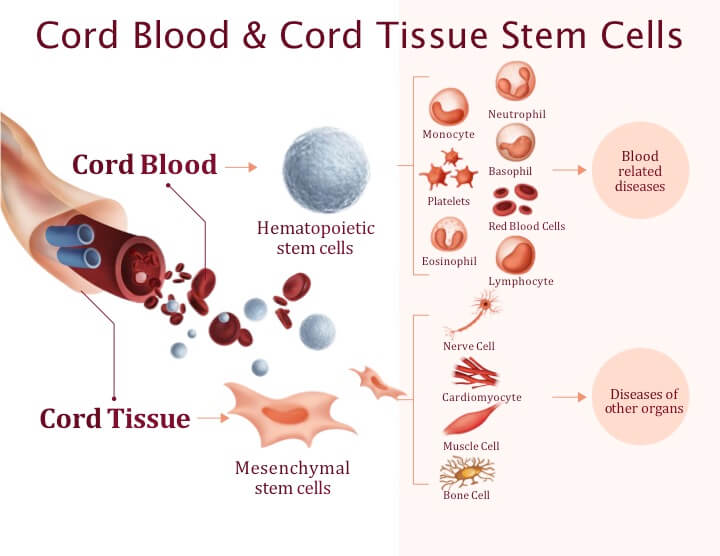 Cord tissue contains another type of stem cells known as mesenchymal stem cells. They act as a medical surveillance team to repair and regenerate the body in special ways.
Cord tissue contains another type of stem cells known as mesenchymal stem cells. They act as a medical surveillance team to repair and regenerate the body in special ways.
Mesenchymal stem cells are being explored to treat diseases involving organs other than the blood system and the immune system.
In summary, both cord blood and cord tissue are sources of stem cells. These stem cells have different properties and are being explored for their therapeutic potential to treat different diseases. By banking both cord blood and cord tissue, you will be ensuring that your child will have access to an extended range of new stem cell therapies that become available in their lifetime.
More topics you might like
Continue your journey by selecting another topic.
What are newborn stem cells and why are they important?
3:45 minutes | Stem cell basics
Understand the different types of stem cell transplants.
5:30 minutes | Stem cell basics
Learn about the exciting new ways stem cells are being explored as a future therapeutic.
5 minutes | Stem cell basics
A Precious Gift of a Lifetime
Registering for stem cell banking takes only a few minutes.
A Precious Gift of a Lifetime
Registering for stem cell banking takes only a few minutes.