Healthcord Webinar Series
Stem cell therapy explained
Duration
5:30 minutes
Category
Stem cell basics
Series
Cord blood banking
Objective
Educational
What you will learn
- What is stem cell therapy?
- Allogenic and autologous transplants
- Sources of stem cells
- How allogeneic transplants work
- Potential drawbacks of allogeneic transplants
Stem cell therapy explained
This lesson will introduce you to how stem cell therapy works, their potential drawbacks and currently available sources of stem cells.
 Stem cell therapy describes the use of stem cells to treat or prevent diseases. Scientists have been using hematopoietic stem cells for over 60 years to treat blood disorders and diseases of the immune system.
Stem cell therapy describes the use of stem cells to treat or prevent diseases. Scientists have been using hematopoietic stem cells for over 60 years to treat blood disorders and diseases of the immune system.
Hematopoietic stem cells are stem cells that give rise to other blood cells and immune cells in our bodies.
Hematopoietic stem cell therapies currently in use can be broadly categorized into two groups: allogeneic stem cell therapies and autologous therapies.
Allogeneic stem cell therapy involves collecting healthy stem cells from a donor and transplanting them into a patient as a treatment option.
Autologous stem cell therapy involves replacing the stem cell of a patient with his or her own healthy stem cells.
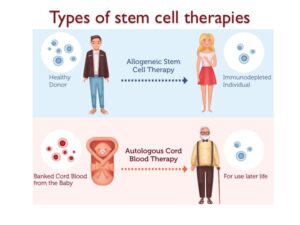 For example, when autologous transplants are used to treat cancer, healthy stem cells, are collected and extracted from a patient prior to chemotherapy.
For example, when autologous transplants are used to treat cancer, healthy stem cells, are collected and extracted from a patient prior to chemotherapy.
Following chemotherapy, damaged stem cells are replaced with the patients’ own healthy stem cells.
According to a survey done by Worldwide Network for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Group in 2012, about 47% of hematopoietic stem cell transplants involved allogeneic stem cell transplant. Before a patient can be treated, you have to find a matching donor to provide a healthy stem cell sample.
The initial stages of an allogeneic transplant involves taking stem cell samples from a donor, either using a blood sample or in a majority of the cases a sample from the bone marrow.
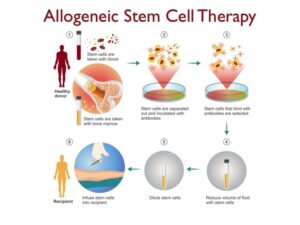 In the next step, stem cells from these samples are purified using specialized antibodies. These selected stem cells are further processed before being transplanted or infused into a patient.
In the next step, stem cells from these samples are purified using specialized antibodies. These selected stem cells are further processed before being transplanted or infused into a patient.
However, there are some of the limitations associated with allogeneic stem cell therapy.
First, it is necessary to find a matching donor, a step that can be extremely difficult.
Even when a matched sample is used, there is a high risk of rejection due to graft versus host disease. This is a case where the immune system of the patient recognizes the transplanted cells as being foreign and starts attacking them. In addition, bone marrow donation involves surgery. It is a surgical procedure, which is invasive even for the donor.
 The final point to consider is that the age of the donor may be relevant because even stem cells age. Studies have compared stem cells from young versus younger donors and noticed significant differences in robustness in these samples. Visit our lesson on stem cells and aging to learn more about this topic.
The final point to consider is that the age of the donor may be relevant because even stem cells age. Studies have compared stem cells from young versus younger donors and noticed significant differences in robustness in these samples. Visit our lesson on stem cells and aging to learn more about this topic.
We will end this lesson by highlighting potential stem cell sources that are available for cell therapies: adult stem cells, induced pluripotent cells and newborn stem cells.
Adult stem cells can be isolated from the bone marrow and a variety of other tissues. Isolating adult stem cells can be difficult because the number of stem cells decrease as we age.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) are being widely explored in the lab. These are stem cells made in the lab by reverse engineering adult cells.
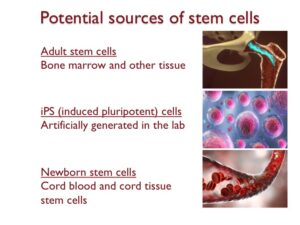 IPS cells have contributed to revolutionary discoveries involving stem cells in the lab. However, the safety and efficacy of using them for cell therapy remains to be established.
IPS cells have contributed to revolutionary discoveries involving stem cells in the lab. However, the safety and efficacy of using them for cell therapy remains to be established.
Cord blood and cord tissue are sources of newborn stem cells. The main limitation here is that these stem cells can only be collected at birth.
Many clinical trials around the world are exploring the possibility of using stem cell therapy to treat a number of prevalent diseases such as diabetes, Alzheimer’s, osteoporosis and arthritis. So, by choosing to save newborn stem cells today, you are providing your child access to these potential revolutionary stem cell therapies that may become available in his/her lifetime.
More topics you might like
Continue your journey by selecting another topic.
What are newborn stem cells and why are they important?
3:45 minutes | Stem cell basics
Discover more about the placenta, cord blood and cord tissue.
4:00 minutes | Stem cell basics
Learn about the exciting new ways stem cells are being explored as a future therapeutic.
5 minutes | Stem cell basics
A Precious Gift of a Lifetime
Registering for stem cell banking takes only a few minutes.
A Precious Gift of a Lifetime
Registering for stem cell banking takes only a few minutes.